 History of C Language
History of C Language
History of C language is interesting to know. Here we are going to discuss brief history of c language.
C programming language was developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie at bell laboratories of AT&T (American Telephone & Telegraph), located in U.S.A.
Dennis Ritchie is known as the founder of c language.
It was developed to overcome the problems of previous languages such as B, BCPL etc.
Initially, C language was developed to be used in UNIX operating system. It inherits many features of previous languages such as B and BCPL.
Let's see the programming languages that were developed before C language.
| Language | Year | Developed By |
|---|---|---|
| Algol | 1960 | International Group |
| BCPL | 1967 | Martin Richard |
| B | 1970 | Ken Thompson |
| Traditional C | 1972 | Dennis Ritchie |
| K & R C | 1978 | Kernighan & Dennis Ritchie |
| ANSI C | 1989 | ANSI Committee |
| ANSI/ISO C | 1990 | ISO Committee |
| C99 | 1999 | Standardization Committee |
Features of C Language
C is the widely used language. It provides a lot of features that are given below.
- Simple
- Machine Independent or Portable
- Mid-level programming language
- structured programming language
- Rich Library
- Memory Management
- Fast Speed
- Pointers
- Recursion
- Extensible
1) Simple
C is a simple language in the sense that it provides structured approach (to break the problem into parts), rich set of library functions, data types etc.
2) Machine Independent or Portable
Unlike assembly language, c programs can be executed in many machines with little bit or no change. But it is not platform-independent.
3) Mid-level prorgramming language
C is also used to do low level programming. It is used to develop system applications such as kernel, driver etc. It also supports the feature of high level language. That is why it is known as mid-level language.
4) Structured prorgramming language
C is a structured programming language in the sense that we can break the program into parts using functions. So, it is easy to understand and modify.
5) Rich Library
C provides a lot of inbuilt functions that makes the development fast.
6) Memory Management
It supports the feature of dynamic memory allocation. In C language, we can free the allocated memory at any time by calling the free() function.
7) Speed
The compilation and execution time of C language is fast.
8) Pointer
C provides the feature of pointers. We can directly interact with the memory by using the pointers. We can use pointers for memory, structures, functions, array etc.
9) Recursion
In c, we can call the function within the function. It provides code reusability for every function.
10) Extensible
C language is extensible because it can easily adopt new features.
First C Program
Before starting the abcd of C language, you need to learn how to write, compile and run the first c program.
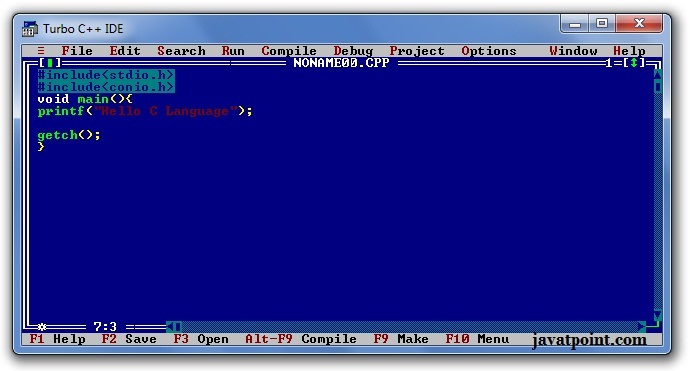
To write the first c program, open the C console and write the following code:
#include <stdio.h> includes the standard input output library functions. The printf() function is defined in stdio.h .
#include <conio.h> includes the console input output library functions. The getch() function is defined in conio.h file.
void main() The main() function is the entry point of every program in c language. The void keyword specifies that it returns no value.
printf() The printf() function is used to print data on the console.
getch() The getch() function asks for a single character. Until you press any key, it blocks the screen.
How to compile and run the c program
There are 2 ways to compile and run the c program, by menu and by shortcut.
By menu
Now click on the compile menu then compile sub menu to compile the c program.
Then click on the run menu then run sub menu to run the c program.
By shortcut
Or, press ctrl+f9 keys compile and run the program directly.
You will see the following output on user screen.

You can view the user screen any time by pressing the alt+f5 keys.
Now press Esc to return to the turbo c++ console.
clear screen by clrscr() function
If you run the c program many times, it will append the output in previous output. But, you can call clrscr() functionto clear the screen. So it will be better for you to call clrscr() function after the main method as given below:
Flow of C Program
The C program follows many steps in execution. To understand the flow of C program well, let us see a simple program first.
File: simple.c
Let's try to understand the flow of above program by the figure given below.

1) C program (source code) is sent to preprocessor first. The preprocessor is responsible to convert preprocessor directives into their respective values. The preprocessor generates an expanded source code.
2) Expanded source code is sent to compiler which compiles the code and converts it into assembly code.
3) The assembly code is sent to assembler which assembles the code and converts it into object code. Now a simple.obj file is generated.
4) The object code is sent to linker which links it to the library such as header files. Then it is converted into executable code. A simple.exe file is generated.
5) The executable code is sent to loader which loads it into memory and then it is executed. After execution, output is sent to console.
printf scanf in C
The printf() and scanf() functions are used for input and output in C language. Both functions are inbuilt library functions, defined in stdio.h (header file).
printf() function
The printf() function is used for output. It prints the given statement to the console.
The syntax of printf() function is given below:
The format string can be %d (integer), %c (character), %s (string), %f (float) etc.
scanf() function
The scanf() function is used for input. It reads the input data from the console.
Variables in C
A variable is a name of memory location. It is used to store data. Its value can be changed and it can be reused many times.It is a way to represent memory location through symbol so that it can be easily identified.Let's see the syntax to declare a variable:The example of declaring variable is given below:Here, a, b, c are variables and int,float,char are data types.We can also provide values while declaring the variables as given below:
Data Types in C
A data type specifies the type of data that a variable can store such as integer, floating, character etc.There are 4 types of data types in C language.
| Types | Data Types |
|---|---|
| Basic Data Type | int, char, float, double |
| Derived Data Type | array, pointer, structure, union |
| Enumeration Data Type | enum |
| Void Data Type | void |
C if else Statement
The if statement in C language is used to perform operation on the basis of condition. By using if-else statement, you can perform operation either condition is true or false.There are many ways to use if statement in C language:
- If statement
- If-else statement
- If else-if ladder
- Nested if
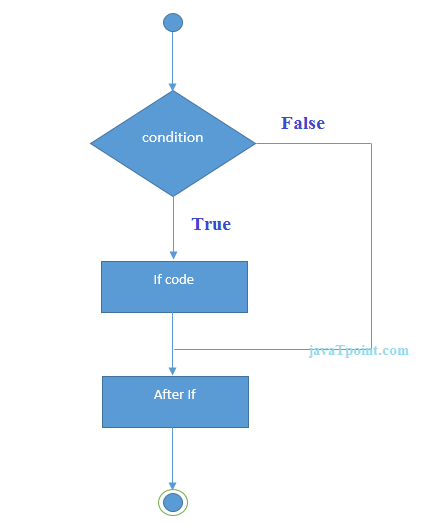
If Statement
The single if statement in C language is used to execute the code if condition is true. The syntax of if statement is given below:Flowchart of if statement in C
Let's see a simple example of c language if statement.
Output
enter a number:4 4 is even number
enter a number:5
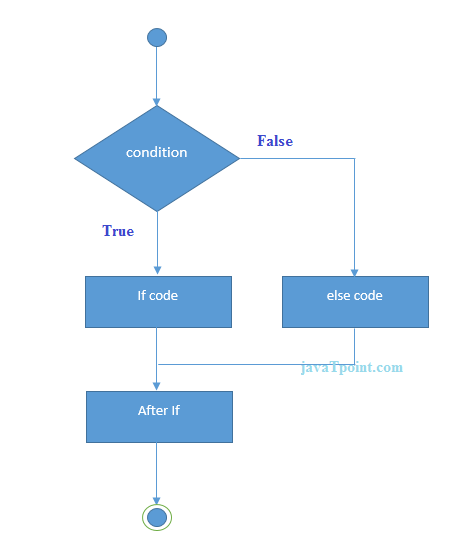
If-else Statement
The if-else statement in C language is used to execute the code if condition is true or false. The syntax of if-else statement is given below:Flowchart of if-else statement in C
Let's see the simple example of even and odd number using if-else statement in C language.
Output
enter a number:4 4 is even number
enter a number:5 5 is odd number
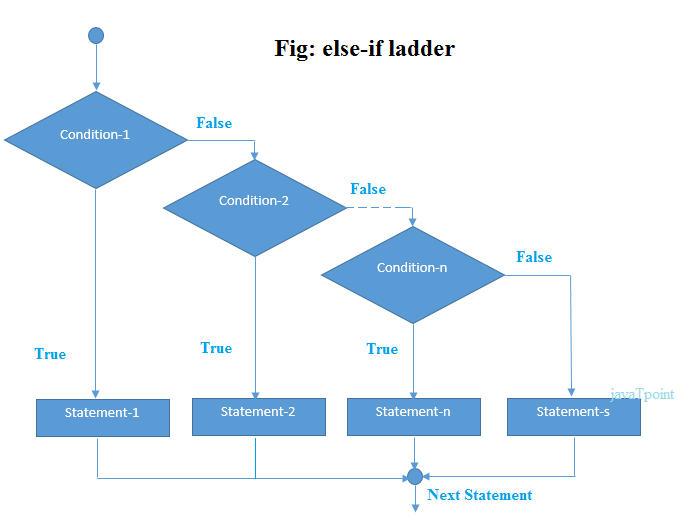
If else-if ladder Statement
The if else-if statement is used to execute one code from multiple conditions. The syntax of if else-if statement is given below:Flowchart of else-if ladder statement in C
The example of if-else-if statement in C language is given below.
Output
enter a number:4 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
enter a number:50 number is equal to 50
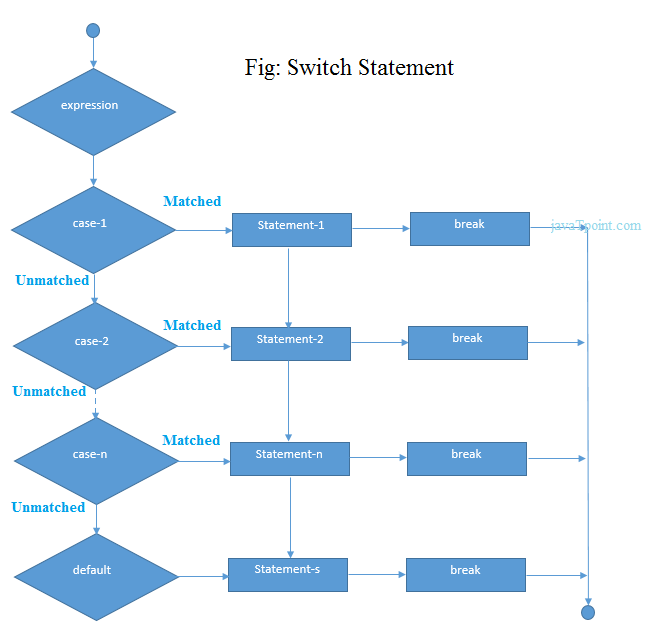
C Switch Statement
The switch statement in C language is used to execute the code from multiple conditions. It is like if else-if ladder statement.The syntax of switch statement in c language is given below:
Rules for switch statement in C language
1) The switch expression must be of integer or character type.2) The case value must be integer or character constant.
3) The case value can be used only inside the switch statement.
4) The break statement in switch case is not must. It is optional. If there is no break statement found in switch case, all the cases will be executed after matching the case value. It is known as fall through state of C switch statement.
Let's try to understand it by the examples. We are assuming there are following variables.
| Valid Switch | Invalid Switch | Valid Case | Invalid Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| switch(x) | switch(f) | case 3; | case 2.5; |
| switch(x>y) | switch(x+2.5) | case 'a'; | case x; |
| switch(a+b-2) | case 1+2; | case x+2; | |
| switch(func(x,y)) | case 'x'>'y'; | case 1,2,3; |
Flowchart of switch statement in C
Let's see a simple example of c language switch statement.
Output
enter a number:4 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
enter a number:50 number is equal to 50
C Switch statement is fall-through
In C language, switch statement is fall through, it means if you don't use break statement in switch case, all the case after matching case will be executed.Let's try to understand the fall through state of switch statement by the example given below.
Output
enter a number:10 number is equals to 10 number is equals to 50 number is equals to 100 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
enter a number:50 number is equal to 50 number is equals to 100 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
C Loops
The loops in C language are used to execute a block of code or a part of the program several times.In other words, it iterates a code or group of code many times.
Why use loops in C language?
Suppose that you have to print table of 2, then you need to write 10 lines of code.By using the loop statement, you can do it by 2 or 3 lines of code only.
Advantage of loops in C
1) It saves code.2) It helps to traverse the elements of array (which is covered in next pages).
Types of C Loops
There are three types of loops in C language that is given below:- do while
- while
- for
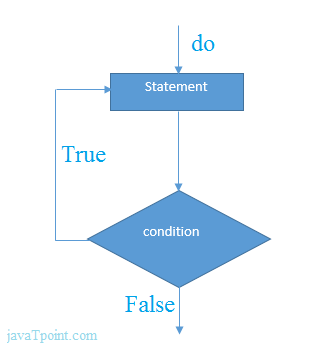
do-while loop in C
It iterates the code until condition is false. Here, condition is given after the code. So at least once, code is executed whether condition is true or false.It is better if you have to execute the code at least once.
The syntax of do-while loop in c language is given below:
Flowchart and Example of do-while loop
while loop in C
Like do while, it iterates the code until condition is false. Here, condition is given before the code. So code may be executed 0 or more times.It is better if number of iteration is not known by the user.
The syntax of while loop in c language is given below:
Flowchart and Example of while loop
for loop in C
Like while, it iterates the code until condition is false. Here, initialization, condition and increment/decrement is given before the code. So code may be executed 0 or more times.It is good if number of iteration is known by the user.
The syntax of for loop in c language is given below:
do while loop in C
To execute a part of program or code several times, we can use do-while loop of C language. The code given between the do and while block will be executed until condition is true.In do while loop, statement is given before the condition, so statement or code will be executed at lease one time. In other words, we can say it is executed 1 or more times.
It is better if you have to execute the code at least once.
do while loop syntax
The syntax of C language do-while loop is given below:Flowchart of do while loop
do while example
There is given the simple program of c language do while loop where we are printing the table of 1.Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Program to print table for the given number using do while loop
Output
Enter a number: 5 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Enter a number: 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100


Comments
Post a Comment